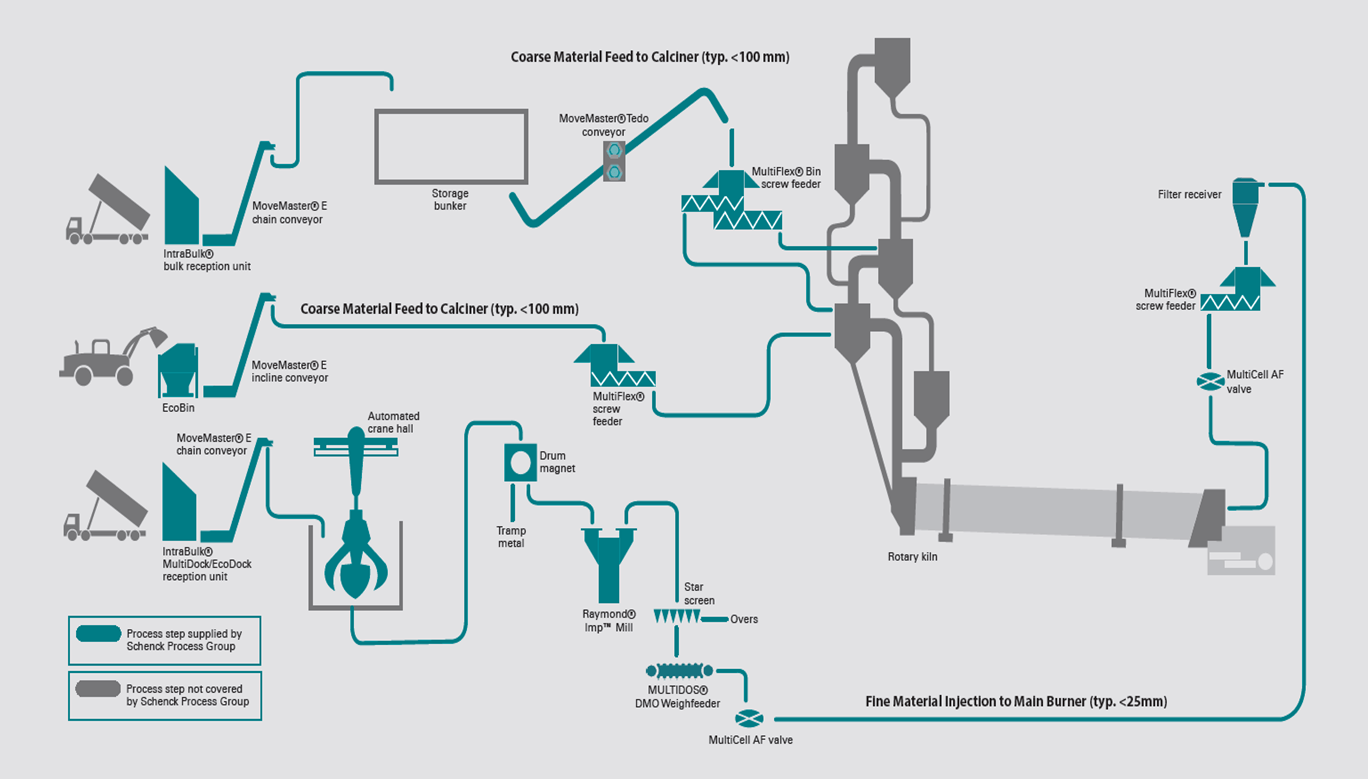
ALTERNATIVE FUEL HANDLING
The cement, steel and power industries are all energy-intensive industries and still predominantly use fossil fuels like coal in their burning process thus releasing carbon dioxide which is damaging to the environment. At the same time, these industries have to comply with increasingly stringent domestic and international legal requirements in order to reduce their CO2 emissions. Alternative fuels play a significant role in achieving these targets.
Alternative fuels can be divided into two groups. The first is biomass, which comprises of wood chips, wood pellets, sunflower seeds, coconut shells, soiled straw or hay and sewage sludge. Biomass is carbon neutral because when burnt, it is only re-releasing the CO2 that it had taken out of the atmosphere whilst growing or being produced.
The second group is comprised of materials such as plastics, tyres, medical refuse, and waste from textile manufacturing, shredded paper or bone meal. In many countries it is no longer permitted to dump plastics, but as the possibilities for recycling are limited, plastic is an appropriate alternative fuel. A particularly suitable application is in the cement industry, where high-temperature processes break up the long chain hydrocarbons which are normally released by burning and can cause health hazards.
AYS together with our technology partners could offers a wide range of products for handling, conveying, weighing and feeding of alternative fuels into process plants:
- Material Receiving Station
- Walking Floor Containers
- Storage Silo for AF and rotating screw discharging system
- Mechanical Conveying for AF eg. Chain Conveyors, Bucket Elevator, Tube or U-Belt Conveyors
- Pneumatic Transport for AF eg. Blow Through Rotary Feeder
- Weighing and dosing equipment for AF eg. Belt Weighfeeder, Screw Weighfeeder MULTIFLEX
Main Material Properties Can Be Summarized As Follows:
Grain size » The coarser the particle, the poorer the flow
Grain shape » The more irregular the particle, the poorer the flow
Bulk density » The lighter the particle, the poorer the flow
Moisture » The moister the particle, the poorer the flow
Grease content » The greasier and stickier the particle, the poorer the flow
Below is an example of a typical material specification for RDF:
| Bulk material: | Waste, shredded |
|---|---|
| Bulk density: | 0.1–0.5 t/m³ |
| Grain size: | 0–60 mm, partially 1–3% to 100 mm |
| Fines: | Max. 2–3% < 300 µm |
| Grain shape: | Two-dimensional, granular |
| Ash content: | Max. 15% |
| Inert materials: | Max. 5% |
| Ferrous and NF metals: | Max. 0.5% |
| Grain size of metal parts: | Max. 40 mm |
| Moisture: | Max. 20% |
| Temperature: | Max. 80°C |
| Flow properties: | Moderate to low viscosity, bridge-forming |
The following acronyms for alternative fuels are frequently used in specifications:
| BRAM | Brennstoff aus Müll (waste-derived fuel) |
|---|---|
| BPG | Brennstoff aus produktionsspezifischen Gewerbeabfällen (fuels derived from production-specific industrial waste) |
| CDR | Combustibile Derivato dai Rifiuti (refuse-derived fuel) |
| EBS | Ersatzbrennstoff (substitute fuel) |
| EWAB | Energy from Waste and Biomass |
| Fluff | Fluffy alternative fuels |
| Flock | Paper industry waste, rejects |
| OTS | Organische Trockensubstanz (organic dry substance) |
| RDF | Refuse Derived Fuel |
| RESH / ASR | Residual shredder materials / Automotive Shredder Residue |
| SBS | Sekundärbrennstoff (secondary fuel) |
| SLF | Shredder Light Fraction |